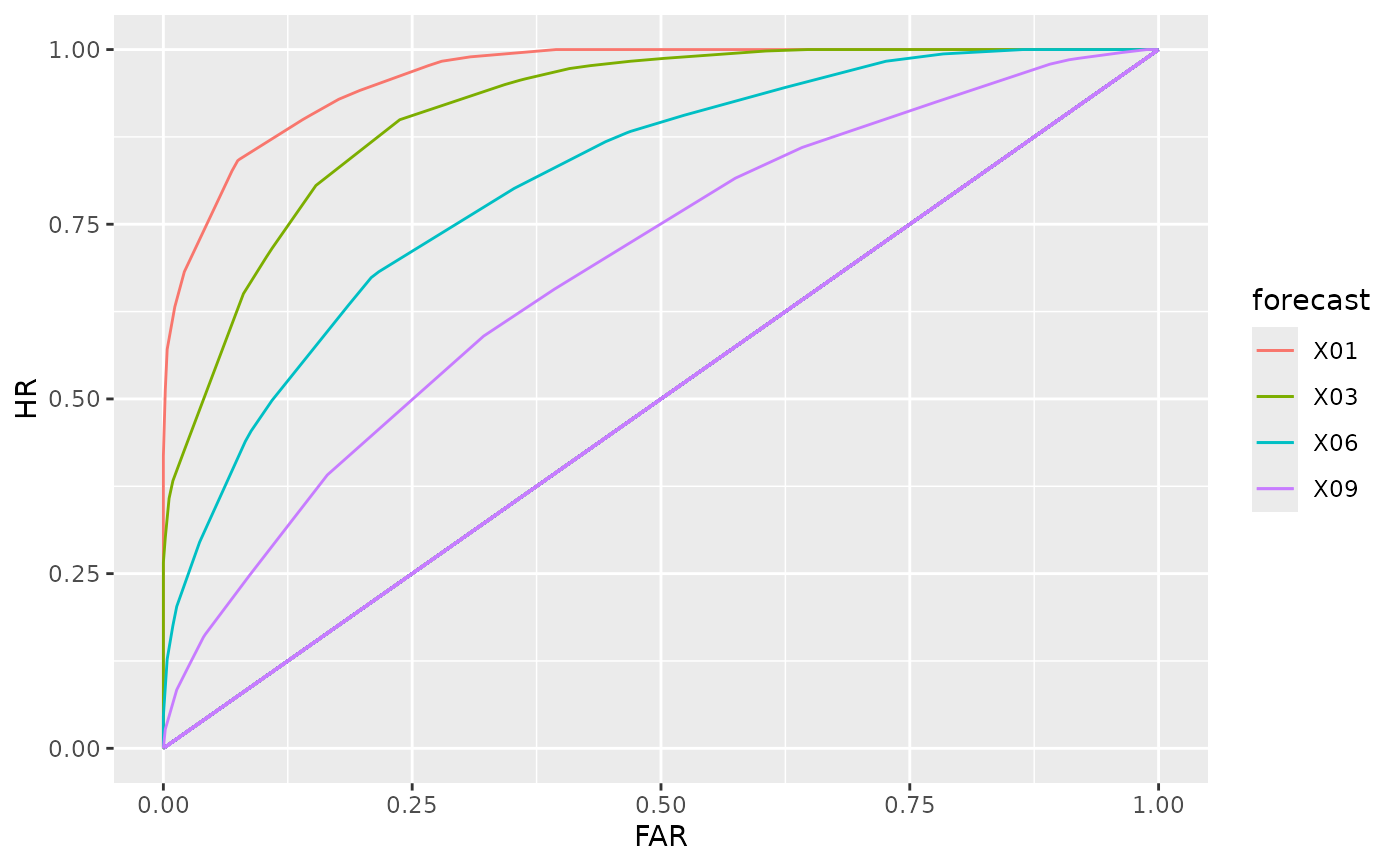
A ROC curve visualizes discrimination ability by displaying the hit rate against the false alarm rate for all threshold values.
Arguments
- x
A data frame, list, matrix, or other object that can be coerced to a tibble. Contains numeric forecasts, and observations (optional).
- y_var
A variable in
xthat contains observations. Specified as the argumentvarindplyr::pull().- ...
Unused.
- y
A numeric vector of observations. If supplied, overrides
y_var. Otherwise, defaults todplyr::pull(x, y_var).- concave
A boolean value indicating whether to calculate the concave hull or the raw ROC diagnostic.
- r
A reference triptych_mcbdsc object whose attributes are used for casting.
Value
A triptych_roc object, that is a vctrs_vctr subclass, and has
a length equal to number of forecasting methods supplied in x. Each entry
is named according to the corresponding forecasting method,
and contains a list of named objects:
estimate: A data frame of hit rates and false rates.region: Either an empty list, or a data frame of pointwise confidence intervals (along diagonal lines with slope \(-\pi_0/\pi_1\)) added byadd_confidence().x: The numeric vector of original forecasts.
Access is most convenient through estimates(), regions(), and forecasts().
See also
Accessors: estimates(), regions(), forecasts(), observations()
Adding uncertainty quantification: add_confidence()
Visualization: plot.triptych_roc(), autoplot.triptych_roc()
Examples
data(ex_binary, package = "triptych")
rc <- roc(ex_binary)
rc
#> <triptych_roc[10]>
#> X01 X02 X03 X04 X05
#> <named list[3]> <named list[3]> <named list[3]> <named list[3]> <named list[3]>
#> X06 X07 X08 X09 X10
#> <named list[3]> <named list[3]> <named list[3]> <named list[3]> <named list[3]>
# 1. Choose 4 predictions
# 2. Visualize
# 3. Adjust the title of the legend
rc[c(1, 3, 6, 9)] |>
autoplot() +
ggplot2::guides(colour = ggplot2::guide_legend("Forecast"))
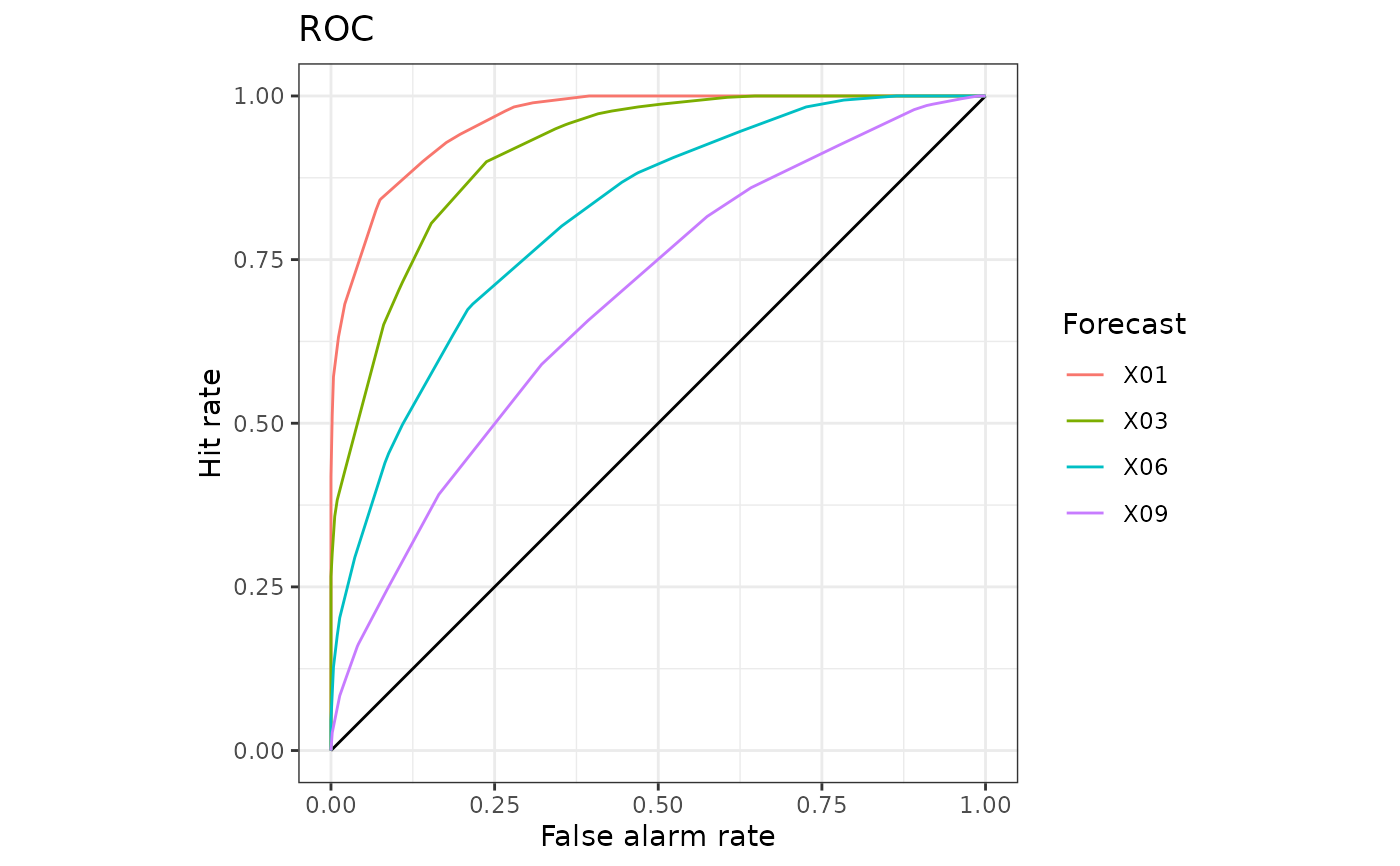 # Build yourself using accessors
library(ggplot2)
df_est <- estimates(rc[c(1, 3, 6, 9)])
ggplot(df_est, aes(x = FAR, y = HR, col = forecast)) +
geom_segment(aes(x = 0, y = 0, xend = 1, yend = 1)) +
geom_path()
# Build yourself using accessors
library(ggplot2)
df_est <- estimates(rc[c(1, 3, 6, 9)])
ggplot(df_est, aes(x = FAR, y = HR, col = forecast)) +
geom_segment(aes(x = 0, y = 0, xend = 1, yend = 1)) +
geom_path()